Fire and corrosion remain two of the greatest threats in the defense industry, concerning the...
How to choose the right corrosion protection for offshore applications: 7 essential steps
Offshore operations exist within a demanding and corrosive environment, therefore it is essential to protect equipment, structures, and assets from corrosion. Corrosion not only compromises the integrity of structures but also poses significant safety and environmental risks. To ensure the longevity and reliability of offshore assets, selecting the right corrosion protection strategy is crucial.
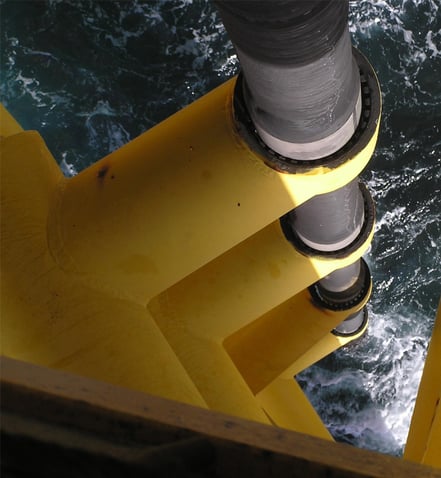

Step 1: Understand the environment
Offshore environments vary from water depth, temperature, and a variety of harsh climate conditions, all contributing to corrosion risk. Before selecting a corrosion protection method, it's important to understand the specific conditions your assets will be exposed to. Consider factors like water salinity, temperature fluctuations, wave action, and exposure to chemicals. This will help you determine the appropriate level of protection needed.
Step 2: Identify corrosion types
Corrosion can occur in different forms, including uniform corrosion, pitting corrosion, crevice corrosion, and galvanic corrosion. Identifying the predominant corrosion types that are likely to affect your assets will guide you towards selecting suitable protection methods.
Step 3: Evaluate Material compatibility
Offshore assets are typically made from a range of materials, each with their own unique sensitivity to corrosion. Whether it's rubber, steel, aluminum, or composites, evaluating material compatibility with potential corrosion protection methods is vital. Some methods may be more effective on certain materials, while others might cause adverse reactions. Ensure the chosen protection method doesn't compromise the structural integrity of the material.
Step 4: Consider Maintenance requirements
Maintenance is a critical consideration that needs to be taken seriously in such a challenging environment. Some corrosion protection methods require regular inspection, maintenance, and replacement. Evaluate the requirements of maintenance in the offshore environment. If routine upkeep is challenging, consider methods that offer longer-lasting protection with minimal intervention.
Step 5: Explore corrosion protection techniques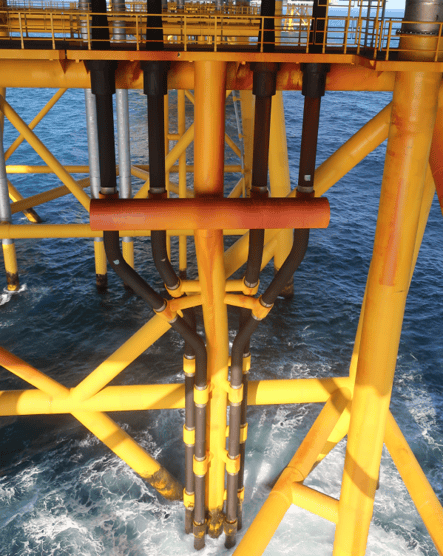
By understanding the pros and cons of each of the technique in relation to your specific needs will help you to make an informed choice. There are multiple corrosion protection techniques available for the offshore application each with their own features.
- Coatings: Barrier coatings like paints and epoxy provide a protective layer between the asset and the corrosive environment, but will often crack because of impact and movements.
- Rubber based corrosion protection: Employing rubber-based coatings can offer an effective shield against corrosion. These coatings, often formulated with elastomers, create a flexible and resilient barrier that can adapt to the asset's movements and environmental stresses, thereby enhancing its longevity in challenging offshore
- Cathodic protection: Utilizes sacrificial anodes or impressed current systems to shift the electrochemical potential, preventing corrosion.
- Corrosion inhibitors: Chemical compounds that mitigate corrosion by forming a protective film on the asset’s surface.
- Cladding and Lining: Applying corrosion-resistant materials to the asset’s surface to create a protective layer.
Step 6: Cost analysis
Corrosion protection methods vary in terms of initial costs, installation expenses, and long-term maintenance. Consider the total cost of ownership over the asset's lifecycle, including expenses related to application, monitoring, and potential downtime due to maintenance. While investing in higher-quality protection might have a higher upfront cost, it could save you substantial expenses in the long run. Opex costs are often very high due to constant maintenance to keep the corrosion away and the equipment in good and safe condition, by using rubber protection when the equipment is new, cost savings can be very high.
Step 7: Regulatory compliance
Offshore operations are subject to strict regulations and environmental standards. Ensure that the corrosion protection method you choose aligns with industry regulations and guidelines. Non-compliance can lead to legal issues, safety concerns, and environmental damage.
Selecting the right corrosion protection strategy for offshore applications is a multifaceted process that requires careful consideration of environmental conditions, material compatibility, maintenance requirements, protection techniques, costs, and compliance. By following these seven steps, you'll be better equipped to safeguard your offshore assets against the detrimental effects of corrosion, ensuring their longevity, safety, and operational efficiency.